| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
An arms race: innate antiviral responses and counteracting viral strategies.
Affiliation
Viral Immune Evasion Group, School of Biochemistry and Immunology, TrinityCollege Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland. schrodem@tcd.ie
Abstract
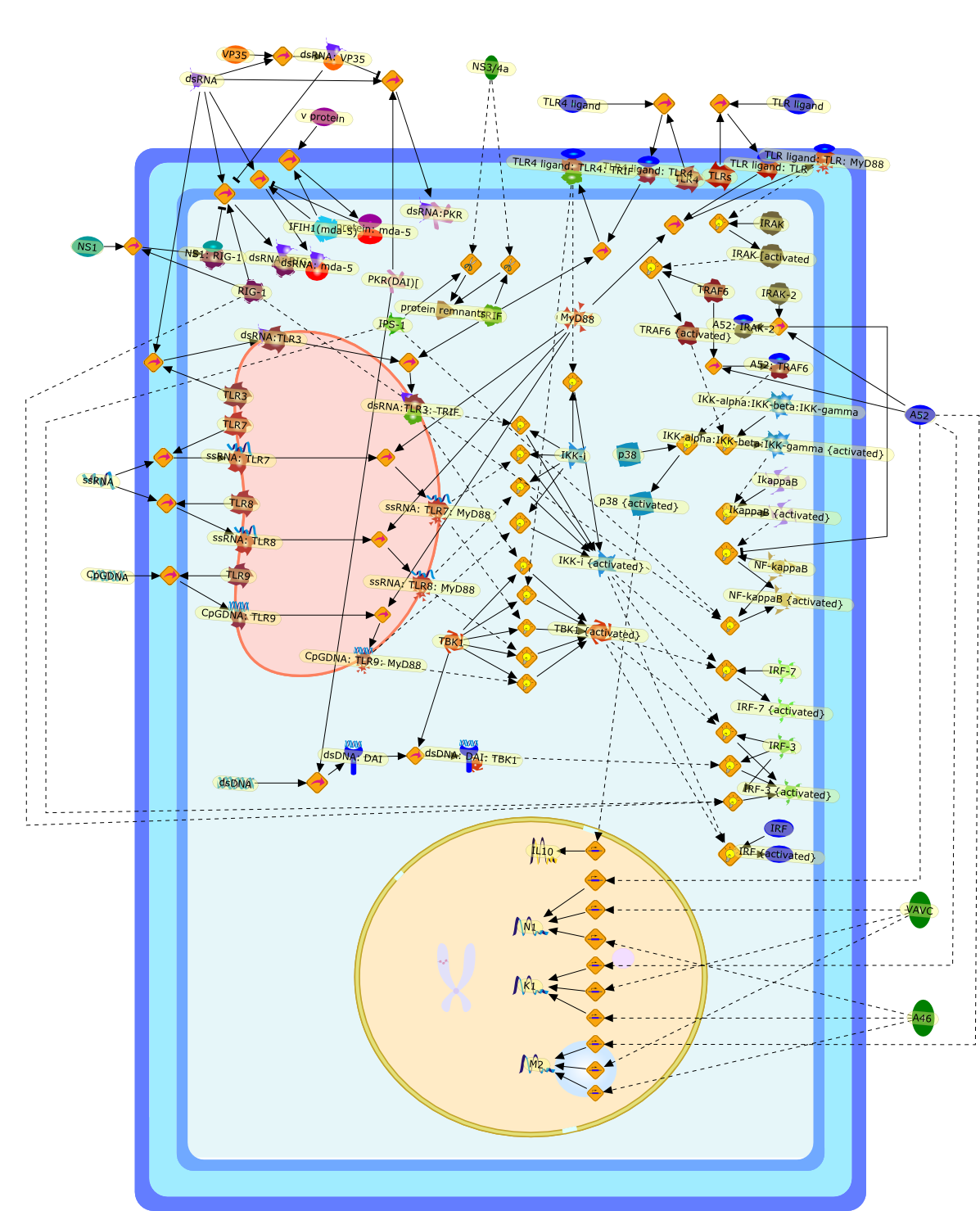
Viral recognition is mediated by different classes of PRRs (pattern-recognitionreceptors) among which the TLRs (Toll-like receptors) and the RLHs [RIG(retinoic-acid-inducible)-like helicases] play major roles. The detection ofPAMPs (pathogen-associated molecular patterns) by these PRRs leads to theinitiation of signalling pathways that ultimately result in the activation oftranscription factors such as NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappaB) and IRF-3 [IFN(interferon) regulatory factor-3] and IRF-7 and the induction ofpro-inflammatory cytokines and type I IFNs. Viruses have evolved a fine-tunedmechanism to evade detection by the immune system or to interfere with theresulting signalling pathways. Here, we discuss viral evasion proteins thatspecifically interfere with TLR and/or RLH signalling.
PMID
18031256
|