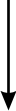| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Interferons at age 50: past, current and future impact on biomedicine.
Affiliation
Taussig Cancer Center, Case Comprehensive Cancer Center, Mellen Center forMultiple Sclerosis, and Lerner Research Institute, The Cleveland Clinic, 9500Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44195, USA. bordene@ccf.org
Abstract
The family of interferon (IFN) proteins has now more than reached the potentialenvisioned by early discovering virologists: IFNs are not only antivirals with aspectrum of clinical effectiveness against both RNA and DNA viruses, but arealso the prototypic biological response modifiers for oncology, and showeffectiveness in suppressing manifestations of multiple sclerosis. Studies ofIFNs have resulted in fundamental insights into cellular signalling mechanisms,gene transcription and innate and acquired immunity. Further elucidation of themultitude of IFN-induced genes, as well as drug development strategies targetingIFN production via the activation of the Toll-like receptors (TLRs), will almostcertainly lead to newer and more efficacious therapeutics. Our goal is to offera molecular and clinical perspective that will enable IFNs or their TLR agonistinducers to reach their full clinical potential.
PMID
18049472
|