| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
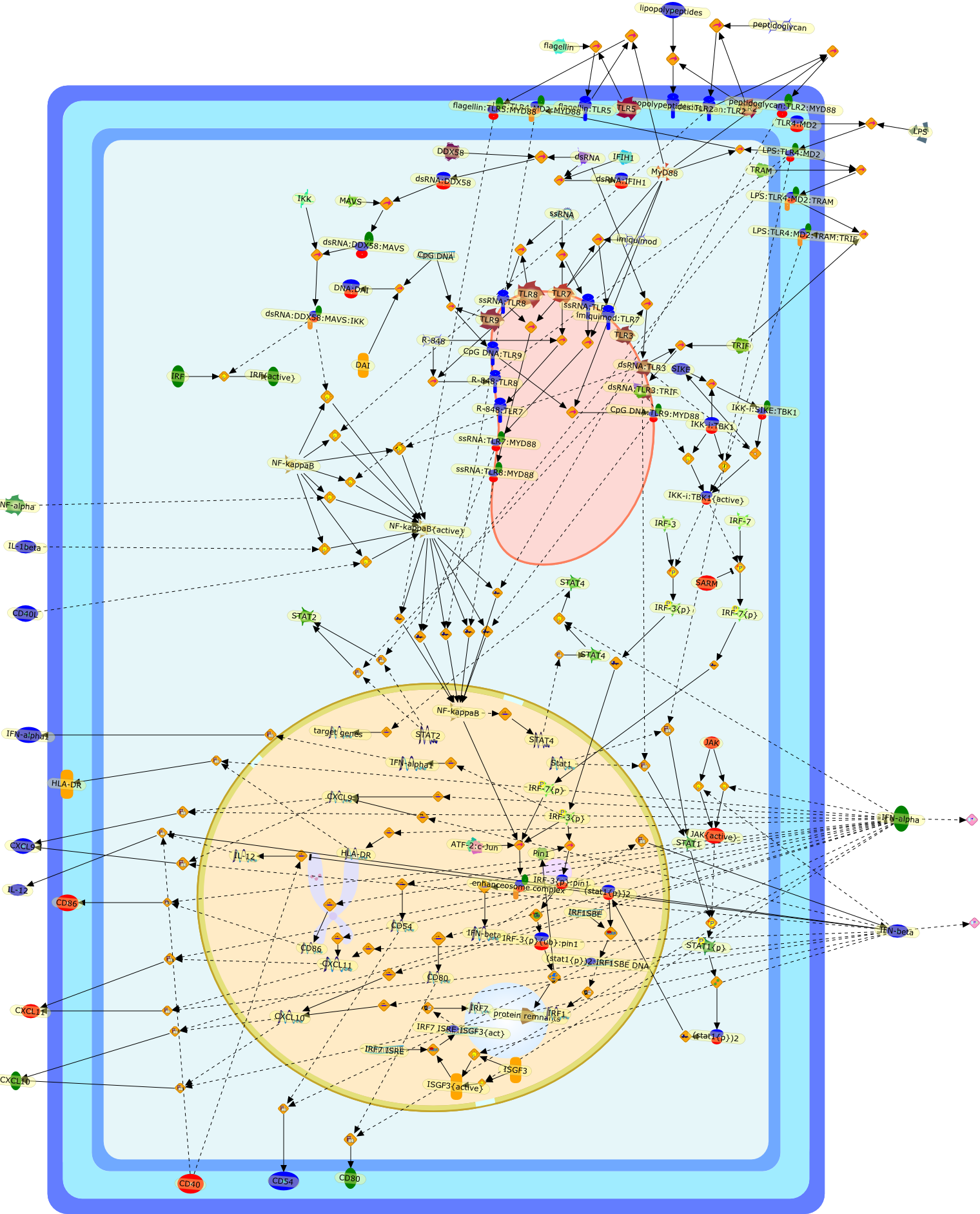
IFN regulation and functions in myeloid dendritic cells.
Affiliation
Department of Infectious, Parasitic and Immune-mediated Diseases, IstitutoSuperiore di Sanita, 00161 Rome, Italy. eliana.coccia@iss.it
Abstract
A central issue in dendritic cells (DC) biology is to understand how type I IFNsmodulate the immuno-regulatory properties of DC. In this review I will addressthis issue in light of the recent experimental evidence on the expression andfunction of these cytokines in myeloid DC. This knowledge may have importanttherapeutic implications in infectious and neoplastic diseases and open newperspectives in the use of IFNs as vaccine adjuvants and in the development ofDC-based vaccines.
PMID
18054516
|