| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
The role of viral nucleic acid recognition in dendritic cells for innate andadaptive antiviral immunity.
Affiliation
Department of Medicine II, Technical University, Ismaninger Str 22, D-81675,Munich, Germany.
Abstract
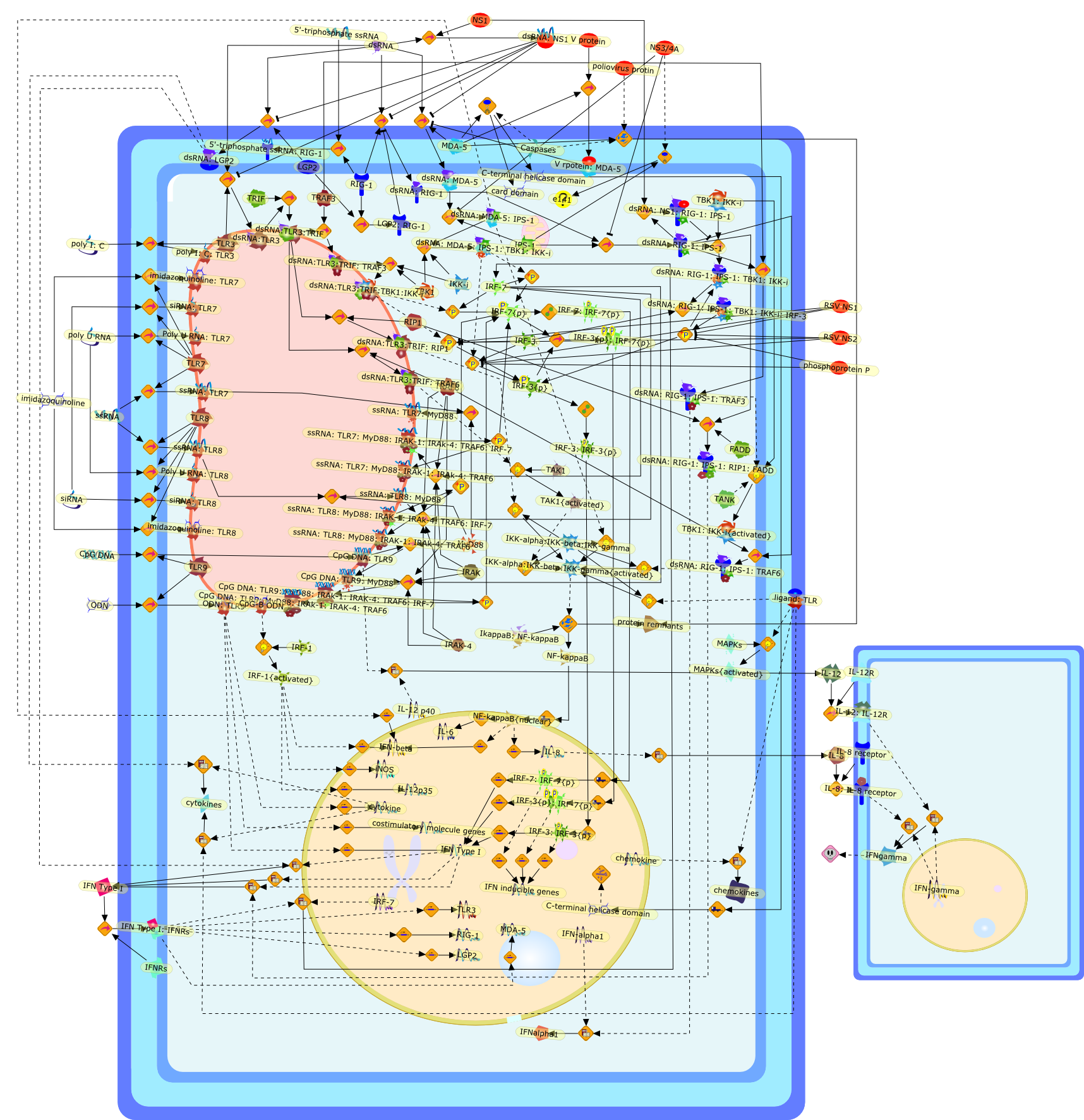
Dendritic cells which are located at the interface of innate and adaptiveimmunity are targets for infection by many different DNA and RNA viruses.Dendritic cell subpopulations express specific nucleic acid recognitionreceptors belonging to the Toll-like receptor family (TLR3, 7, 8, 9) and thecytosolic RNA helicase family (RIG-I, MDA5, LGP2). Activation of dendritic cellsby viral DNA and RNA via these receptors is essential for triggering the innateantiviral immune response and shaping the ensuing adaptive antiviral immunity.This review will summarize our current knowledge of viral nucleic acidrecognition and signaling by Toll-like receptors and RNA helicases focusing onrecent evidence for their specific functions in antiviral defense in vivo.
PMID
18086372
|