| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
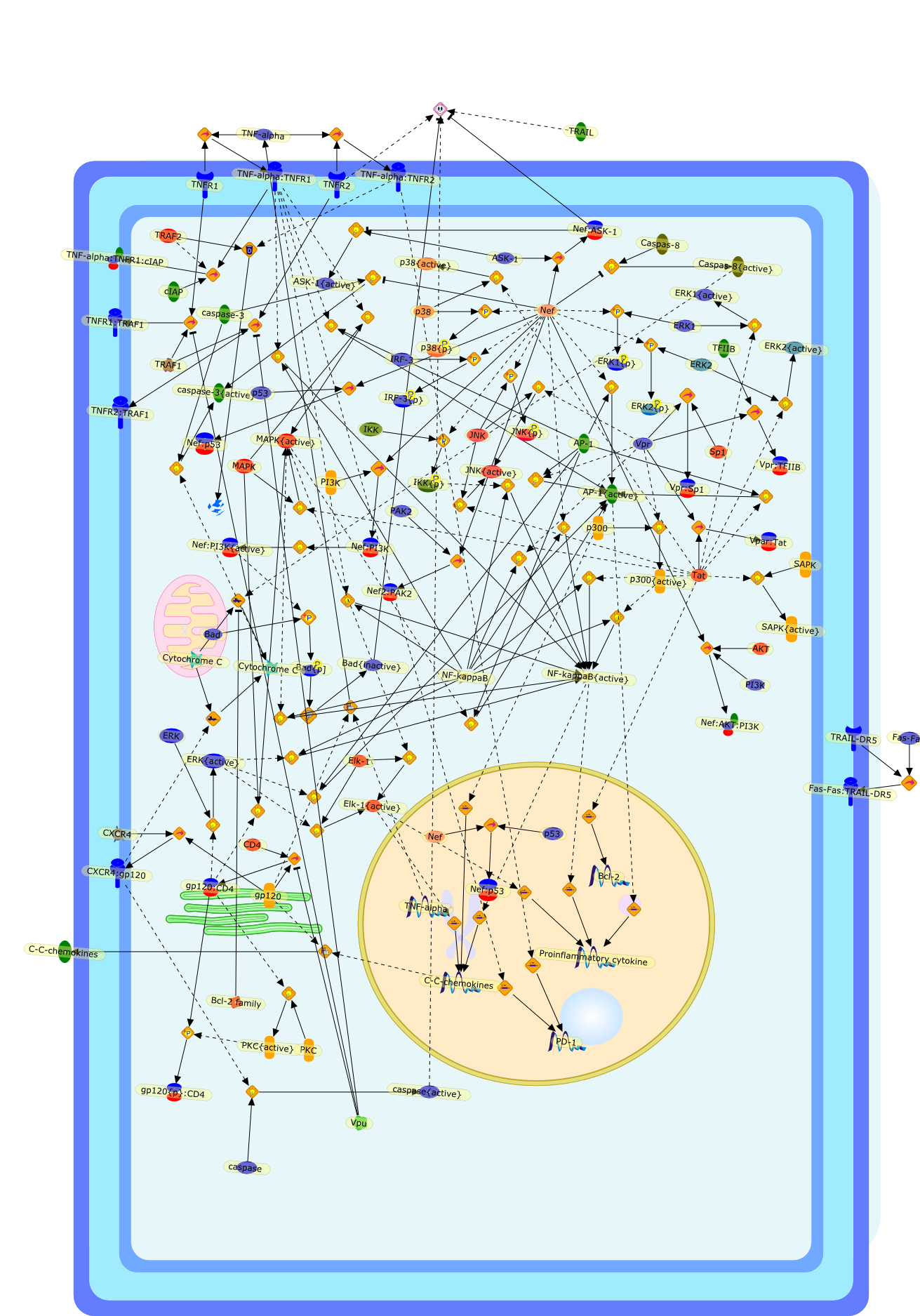
Is HIV infection a TNF receptor signalling-driven disease?
Affiliation
Department of Virology, EA3186, IFR133, Franche-Comte University, HopitalSaint-Jacques, Besancon Cedex, France. gherbein@chu-besancon.fr
Abstract
Recent studies indicate that TNF (tumor necrosis factor) receptor signalling isa key player in HIV infection. HIV proteins have been shown to target TNFreceptor signalling, leading both to apoptosis of uninfected bystander T cellsand to sustained viral replication in infected T cells and macrophages. Thisarticle proposes a model that highlights the role of HIV proteins in themodulation of TNF receptor signalling and could explain both immune suppressionand the formation of viral reservoirs during HIV infection.
PMID
18178131
|