| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
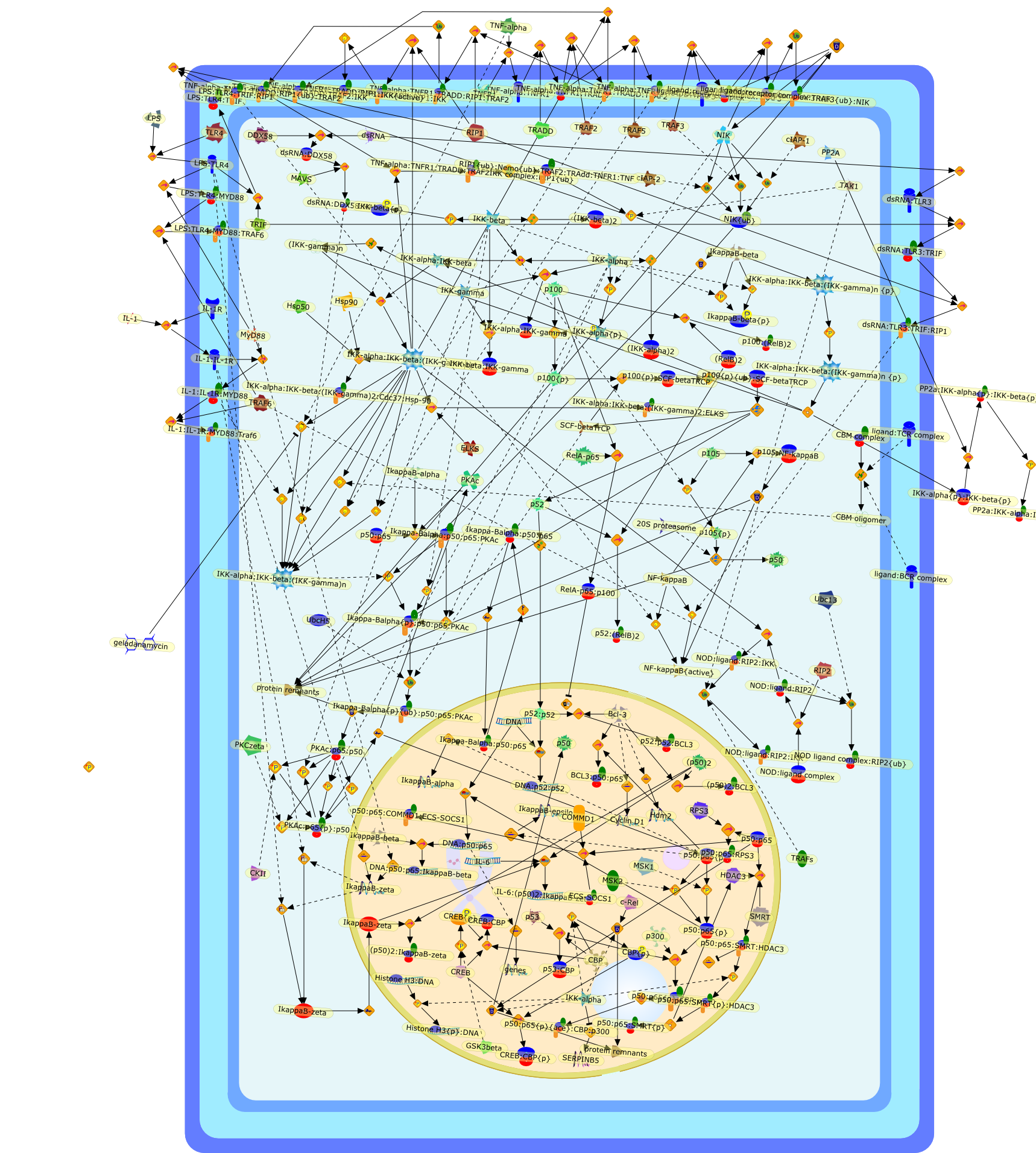
Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling.
Affiliation
Department of Immunobiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT06510, USA.
Abstract
The transcription factor NF-kappaB has served as a standard for inducibletranscription factors for more than 20 years. The numerous stimuli that activateNF-kappaB, and the large number of genes regulated by NF-kappaB, ensure thatthis transcription factor is still the subject of intense research. Here, weattempt to synthesize some of the basic principles that have emerged fromstudies of NF-kappaB, and we aim to generate a more unified view of NF-kappaBregulation.
PMID
18267068
|