| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
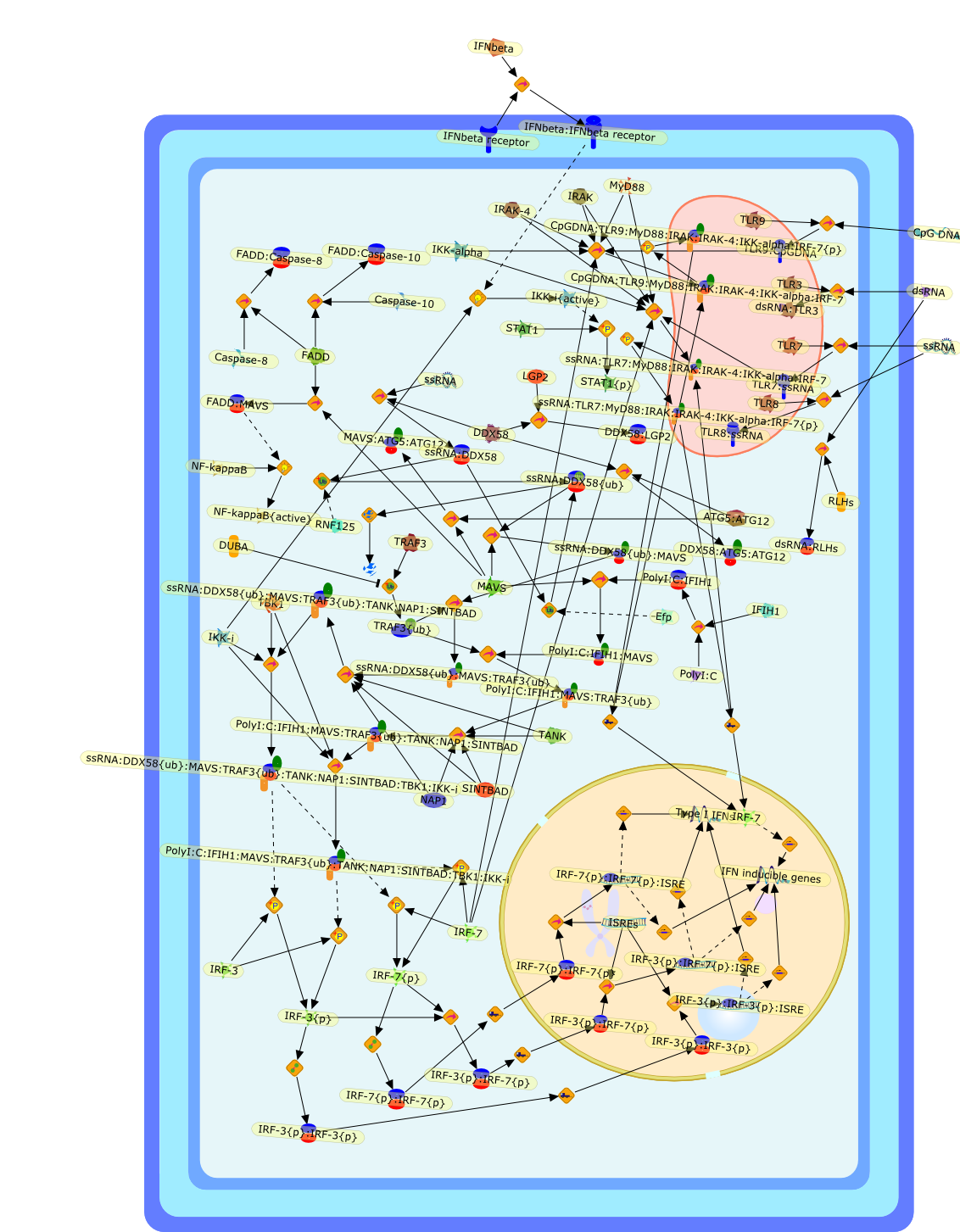
MDA5/RIG-I and virus recognition.
Affiliation
Laboratory of Host Defense, WPI Immunology Frontier Research Center, OsakaUniversity, 3-1 Yamada-oka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan.
Abstract
The innate immune system initially recognizes RNA virus infection and evokesantiviral responses by producing type I interferons (IFNs). Toll-like receptors(TLRs) and cytoplasmic retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like helicases(RLHs) are the two major receptor systems for detecting RNA viruses. The RLHsignaling pathways play essential roles in the recognition of RNA viruses invarious cells, with the exception of plasmacytoid dendritic cells, which utilizeTLRs for virus recognition. The route of infection determines the cell typesresponsible for type I IFN production. Recent studies have suggested that TLRsare critical for activation of adaptive immune responses against several virusinfections, although it may be premature to draw such a conclusion for virusinfections in general. In this review, we will discuss recent advances towardclarifying the signaling pathways activated by RLHs and TLRs.
PMID
18272355
|