| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Toll-like receptors regulation of viral infection and disease.
Affiliation
Department of Immunobiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT06520, USA.
Abstract
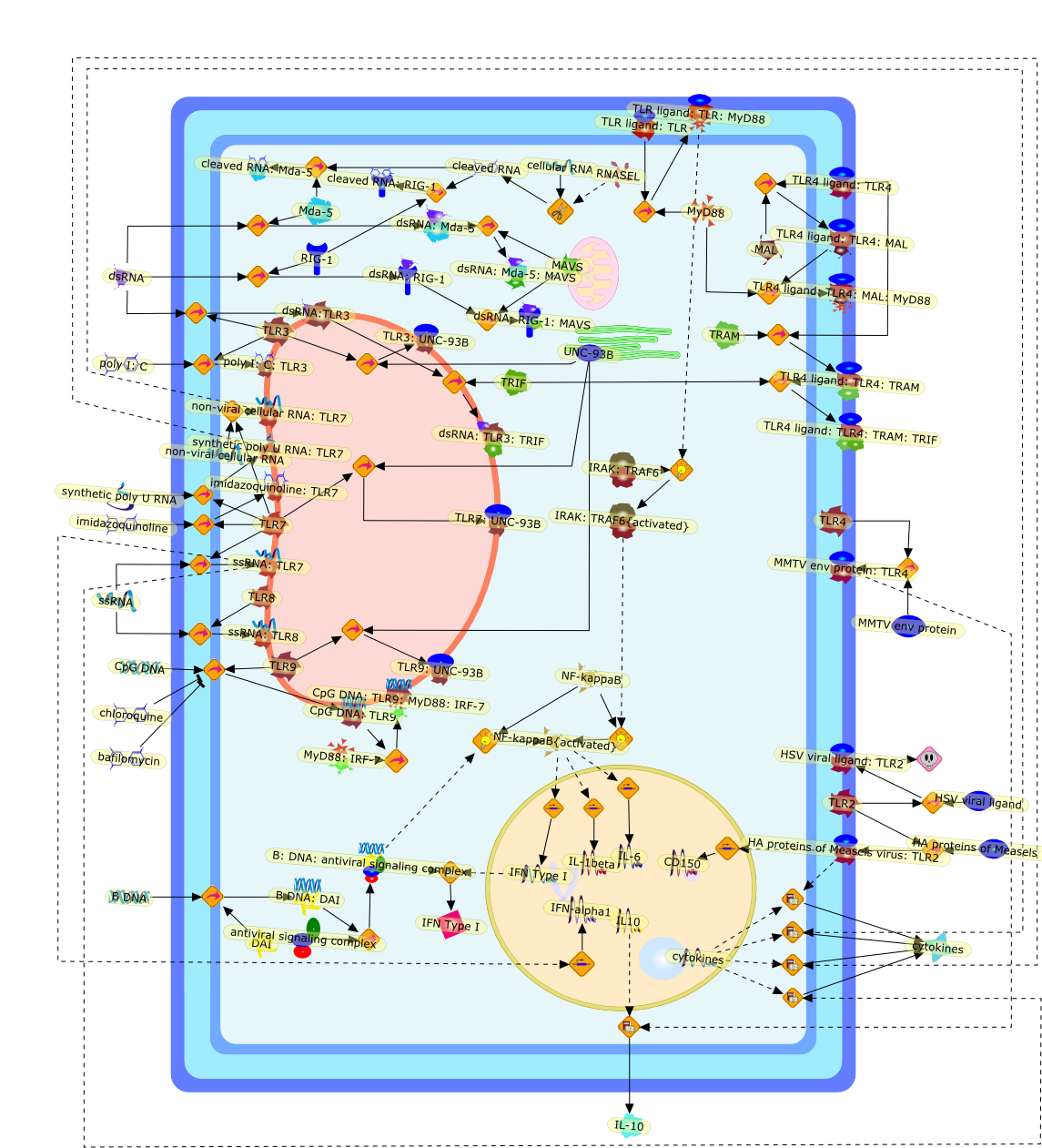
In recent years, it has become increasingly evident that mammalian Toll-likereceptors (TLRs) play a critical role in determining the outcome of virusinfection. TLRs have evolved to recognize viral nucleic acids, and promote thestimulation of innate and adaptive immune responses. Interestingly, the study ofmice harboring deficiencies in various TLR proteins and their adaptors suggeststhat TLR activation promotes protective anti-viral immunity in some cases, whileexacerbating virus-induced disease in others. In this report we describe theinteractions of viruses with both the TLR system and the intracellularrecognition system and highlight the role of TLRs in shaping the outcome ofvirus infection in both a positive and negative manner.
PMID
18280610
|