| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Regulation of endogenous apolipoprotein E secretion by macrophages.
Affiliation
Macrophage Biology Group, Centre for Vascular Research, Room 405C Wallace WurthBuilding, University of New South Wales, High Street, Kensington, Sydney, NSW2050, Australia.
Abstract
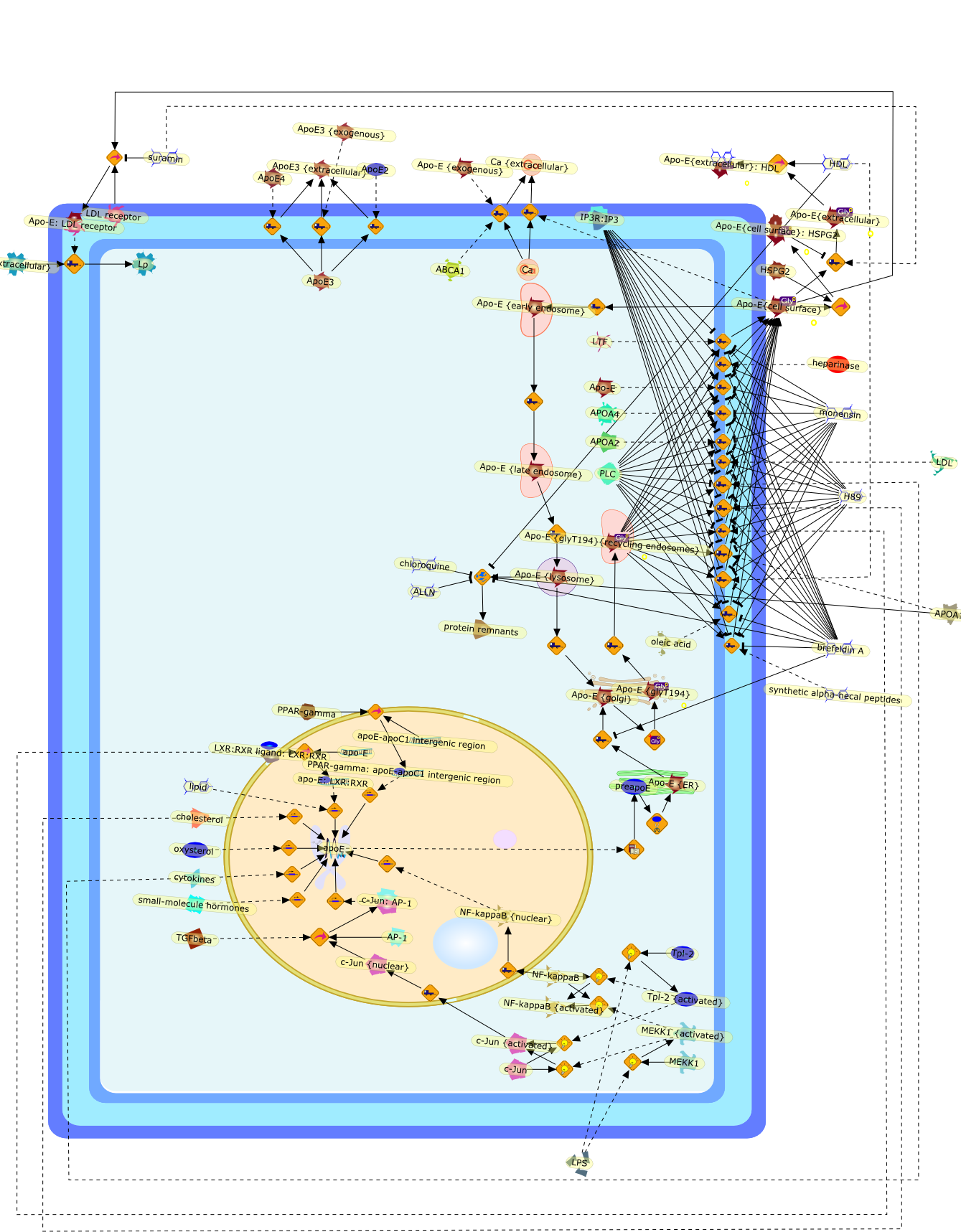
Apolipoprotein E has critical roles in the protection against atherosclerosisand is understood to follow the classical constitutive secretion pathway. Recentstudies have indicated that the secretion of apoE from macrophages is aregulated process of unexpected complexity. Cholesterol acceptors such asapolipoprotein A-I, high density lipoprotein, and phospholipid vesicles canstimulate apoE secretion. The ATP binding cassette transporter ABCA1 is involvedin basal apoE secretion and in lipidating apoE-containing particles secreted bymacrophages. However, the stimulation of apoE secretion by apoA-I isABCA1-independent, indicating the existence of both ABCA1-dependent and-independent pathways of apoE secretion. The release of apoE under basalconditions is also regulated, requiring intact protein kinase A activity,intracellular calcium, and an intact microtubular network. Mathematical modelingof apoE turnover indicates that whereas some pools of apoE are committed toeither secretion or degradation, other pools can be diverted from degradationtoward secretion. Targeted inhibition or stimulation of specific apoEtrafficking pathways will provide unique opportunities to regulate the biologyof this important molecule.
PMID
18388328
|