| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
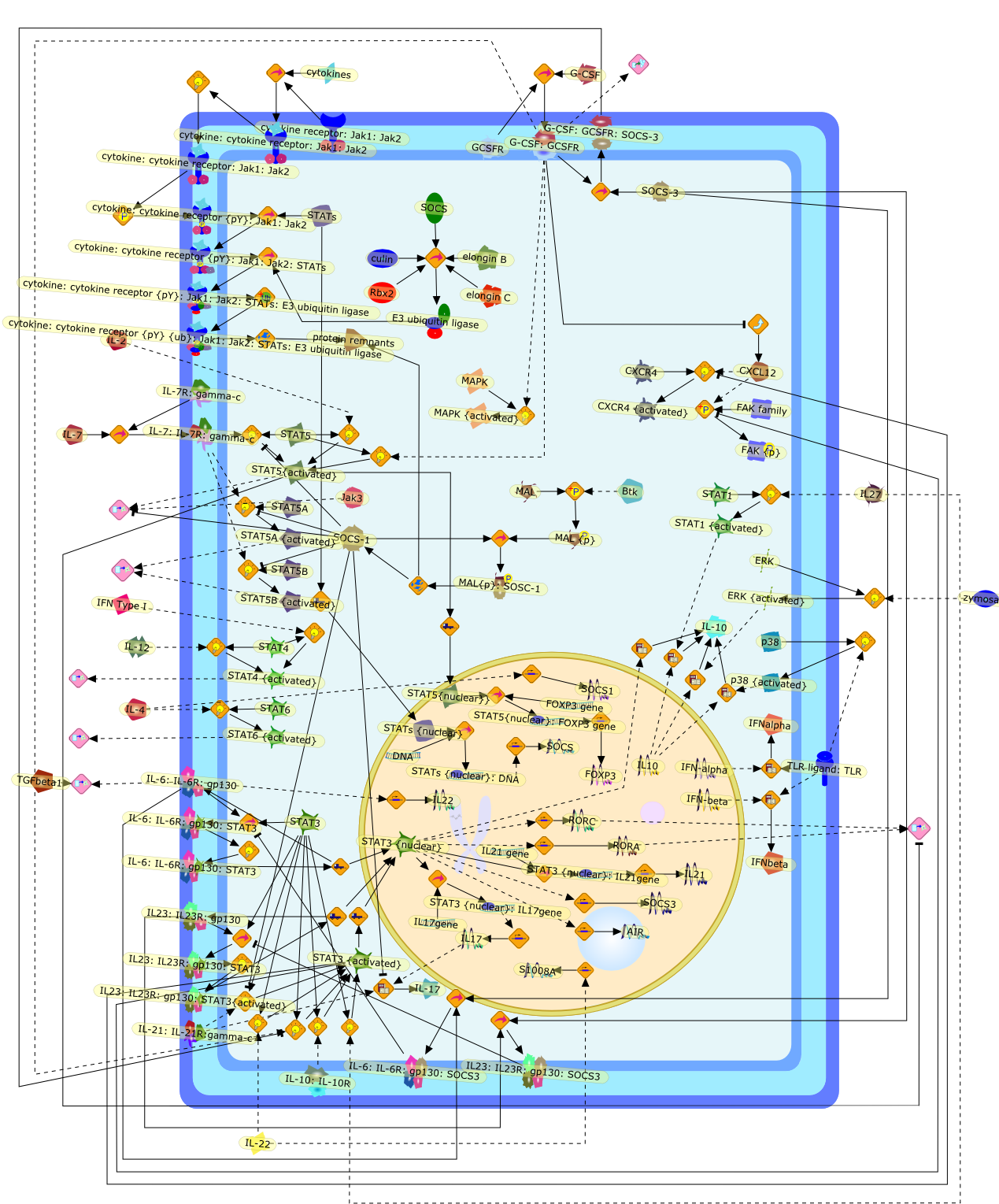
Cytokine signaling modules in inflammatory responses.
Affiliation
Molecular Immunology and Inflammation Branch, National Institute of Arthritis,Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD20852, USA. osheajo@mail.nih.gov
Abstract
Cytokine signaling via a restricted number of Jak-Stat pathways positively andnegatively regulates all cell types involved in the initiation, propagation, andresolution of inflammation. Here, we focus on Jak-Stat signaling in three majorcell types involved in inflammatory responses: T cells, neutrophils, andmacrophages. We summarize how the Jak-Stat pathways in these cells arenegatively regulated by the Suppressor of cytokine signaling (Socs) proteins. Weemphasize that common Jak-Stat-Socs signaling modules can have diversedevelopmental, pro- and anti-inflammatory outcomes depending on the cytokinereceptor activated and which genes are accessible at a given time in a cell'slife. Because multiple components of Jak-Stat-Socs pathways are mutated orclosely associated with human inflammatory diseases, and cytokine-basedtherapies are increasingly deployed to treat inflammation, understandingcytokine signaling will continue to advance our ability to manipulate chronicand acute inflammatory diseases.
PMID
18400190
|