| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Regulation of innate immunity by suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)proteins.
Affiliation
Department of Hygiene and Medical Microbiology, Institute of Hygiene, Universityof Heidelberg, Im Neuenheimer Feld 324, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany.alexander.dalpke@med.uni-heidelberg.de
Abstract
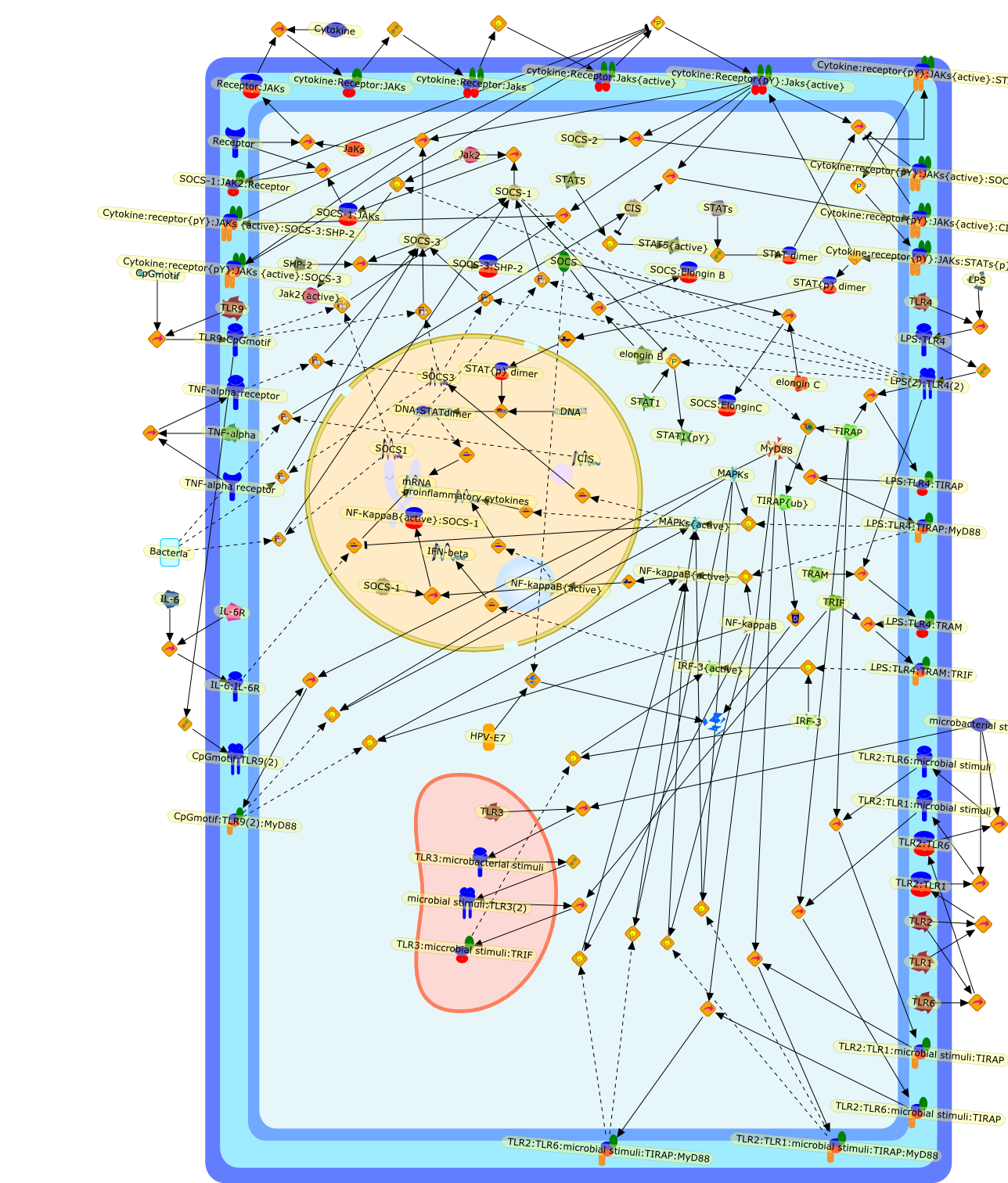
Innate immunity represents the first line of defense against invading pathogens.Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are important for activation of innate immunity.Moreover, cytokines mediate communication of cells and are necessary to mount anappropriately regulated immune response. However, activation of innate immunityhas to be tightly controlled to avoid overshooting immune reactions. Suppressorof cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins have been identified as inducible feedbackinhibitors of cytokine receptors and have been shown to be of crucial importancefor the limitation of inflammatory responses. In this review, we describe therole of SOCS proteins in macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs). Based on our ownfindings, we show that SOCS proteins are directly induced by stimulation ofTLRs. However, SOCS proteins do not interfere with direct TLR signaling, butavoid overshooting activation by regulating paracrine IFN-beta signaling. Inaddition, SOCS proteins in macrophages and DCs regulate the sensitivity towardsIFN-gamma and GM-CSF, thereby modulating anti-microbial activity of macrophagesand differentiation of DCs. We discuss that SOCS induction can also be used bymicrobes to evade immune defense, and this is exemplified by the parasiteToxoplasma gondii which induces SOCS1 to inhibit IFN-gamma-mediated macrophageactivation. Taken together, the findings indicate that SOCS proteins play animportant role in the balanced activation of innate immunity during infectiousencounter.
PMID
18406369
|