| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Developmental plasticity of lymphocytes.
Affiliation
Universidad de Salamanca, Campus Miguel de Unamuno, 37007 Salamanca, Spain.
Abstract
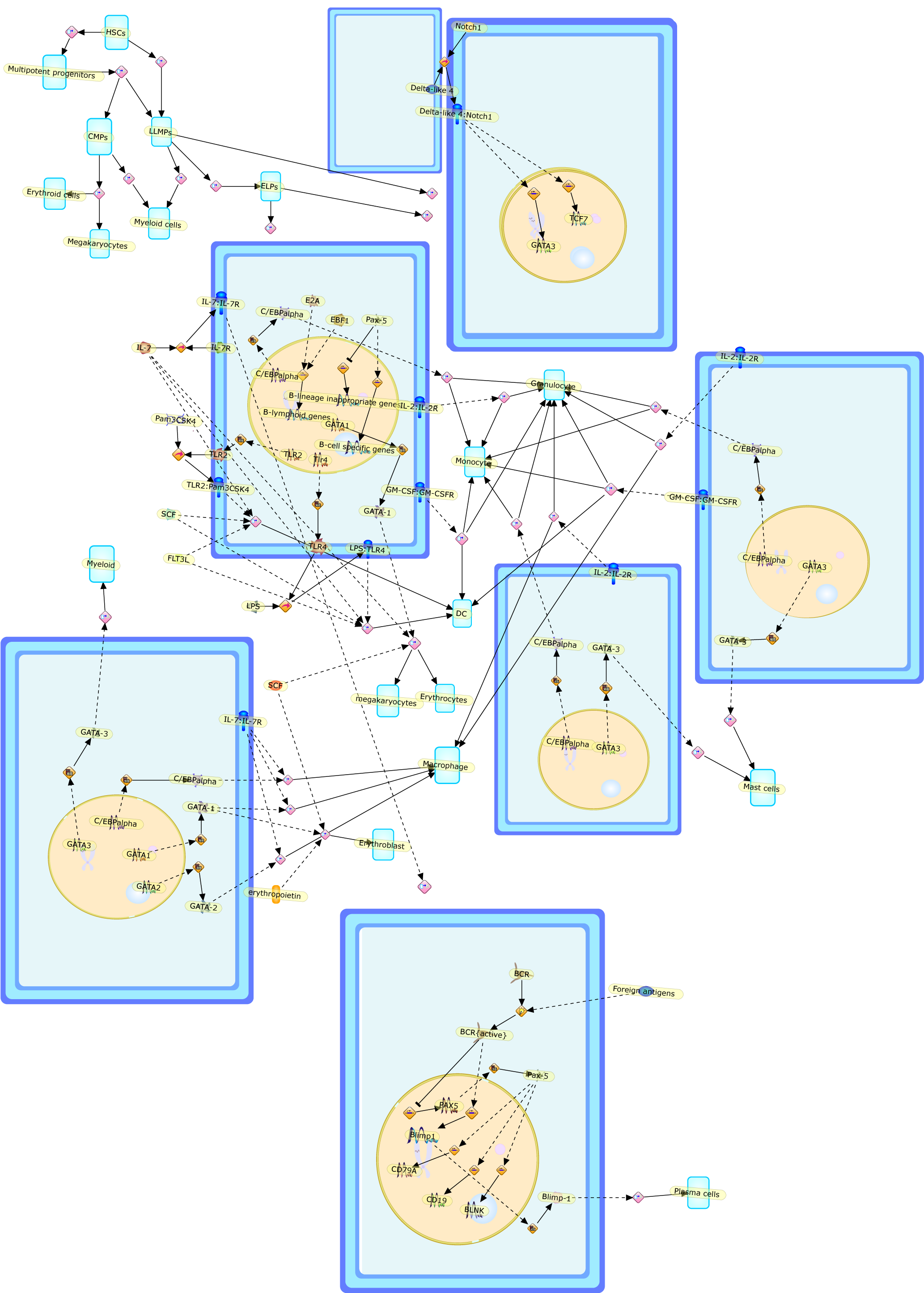
Experimental perturbation of signaling or transcription factor networks has beenused to study the developmental potential of lymphoid progenitors,lineage-committed precursors and mature lymphocytes. Common lymphoid progenitorsand uncommitted pro-T cells can be efficiently diverted into myeloid orerythroid lineages by ectopic cytokine signaling or retroviral expression of themyeloid C/EBPalpha or erythroid GATA1 transcription factor. Forced C/EBPalphaexpression furthermore induces direct transdifferentiation of immaturethymocytes or B cells into macrophages. Notably, conditional inactivation of theB cell commitment factor Pax5 is sufficient to convert mature B cells intofunctional T cells via dedifferentiation to uncommitted progenitors. Togetherthese experiments have uncovered an unanticipated developmental plasticity oflymphocytes, which may account for lineage switches observed in humanmalignancies.
PMID
18472258
|