| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Calcium signaling in lymphocytes.
Affiliation
Department of Pathology, Harvard Medical School, Immune Disease Institute,Boston, MA 02115, USA.
Abstract
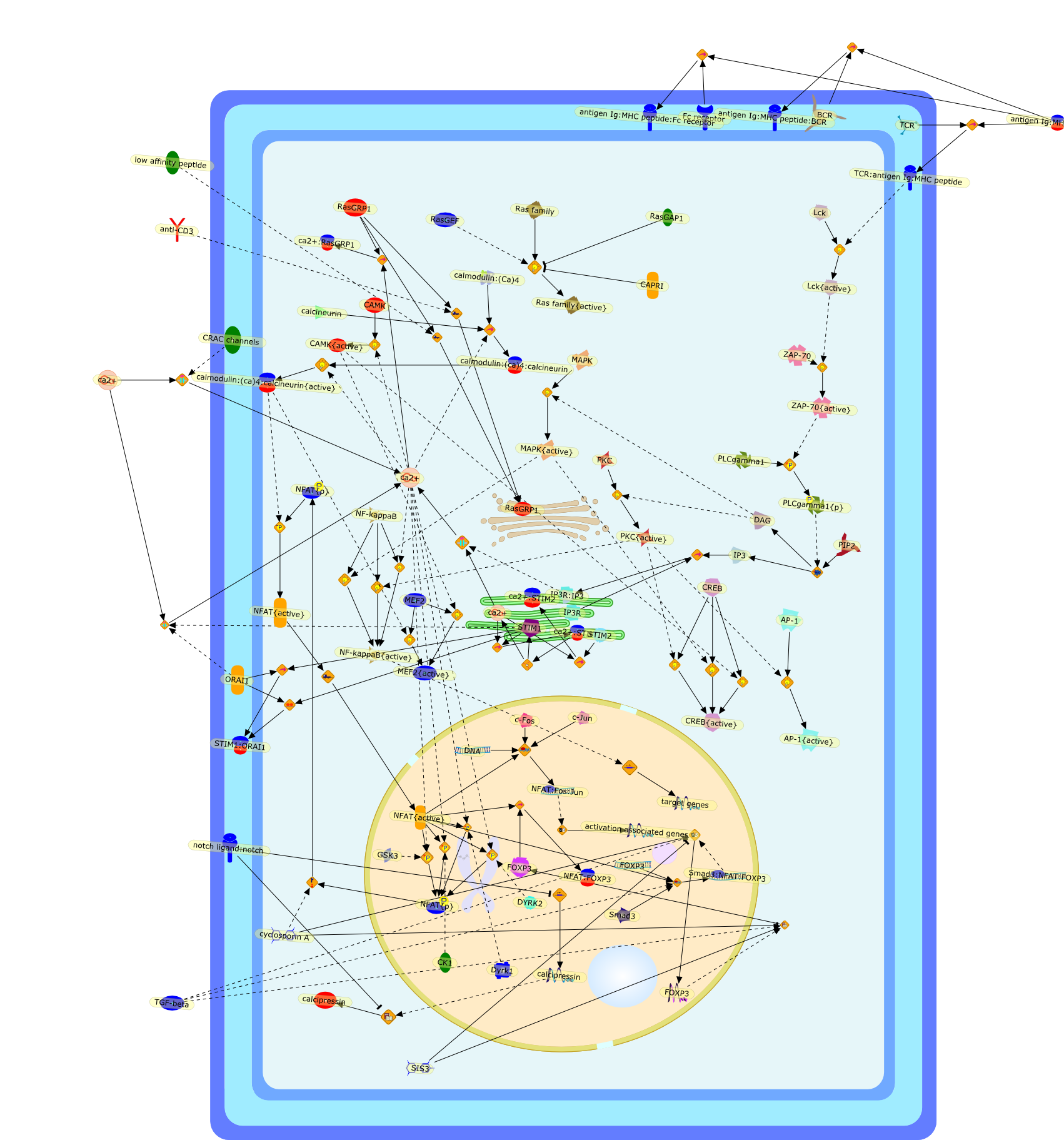
In cells of the immune system, calcium signals are essential for diversecellular functions including differentiation, effector function, and genetranscription. After the engagement of immunoreceptors such as T-cell and B-cellantigen receptors and the Fc receptors on mast cells and NK cells, theintracellular concentration of calcium ions is increased through the sequentialoperation of two interdependent processes: depletion of endoplasmic reticulumCa(2+) stores as a result of binding of inositol trisphosphate (IP(3)) to IP(3)receptors, followed by 'store-operated' Ca(2+) entry through plasma membraneCa(2+) channels. In lymphocytes, mast cells and other immune cell types,store-operated Ca(2+) entry through specialized Ca(2+) release-activated calcium(CRAC) channels constitutes the major pathway of intracellular Ca(2+) increase.A recent breakthrough in our understanding of CRAC channel function is theidentification of stromal interaction molecule (STIM) and ORAI, two essentialregulators of CRAC channel function. This review focuses on the signalingpathways upstream and downstream of Ca(2+) influx (the STIM/ORAI andcalcineurin/NFAT pathways, respectively).
PMID
18515054
|