| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Regulation of mitochondrial antiviral signaling pathways.
Affiliation
Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Lineberger Comprehensive CancerCenter, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC 27599,USA. cbmoore2@med.unc.edu
Abstract
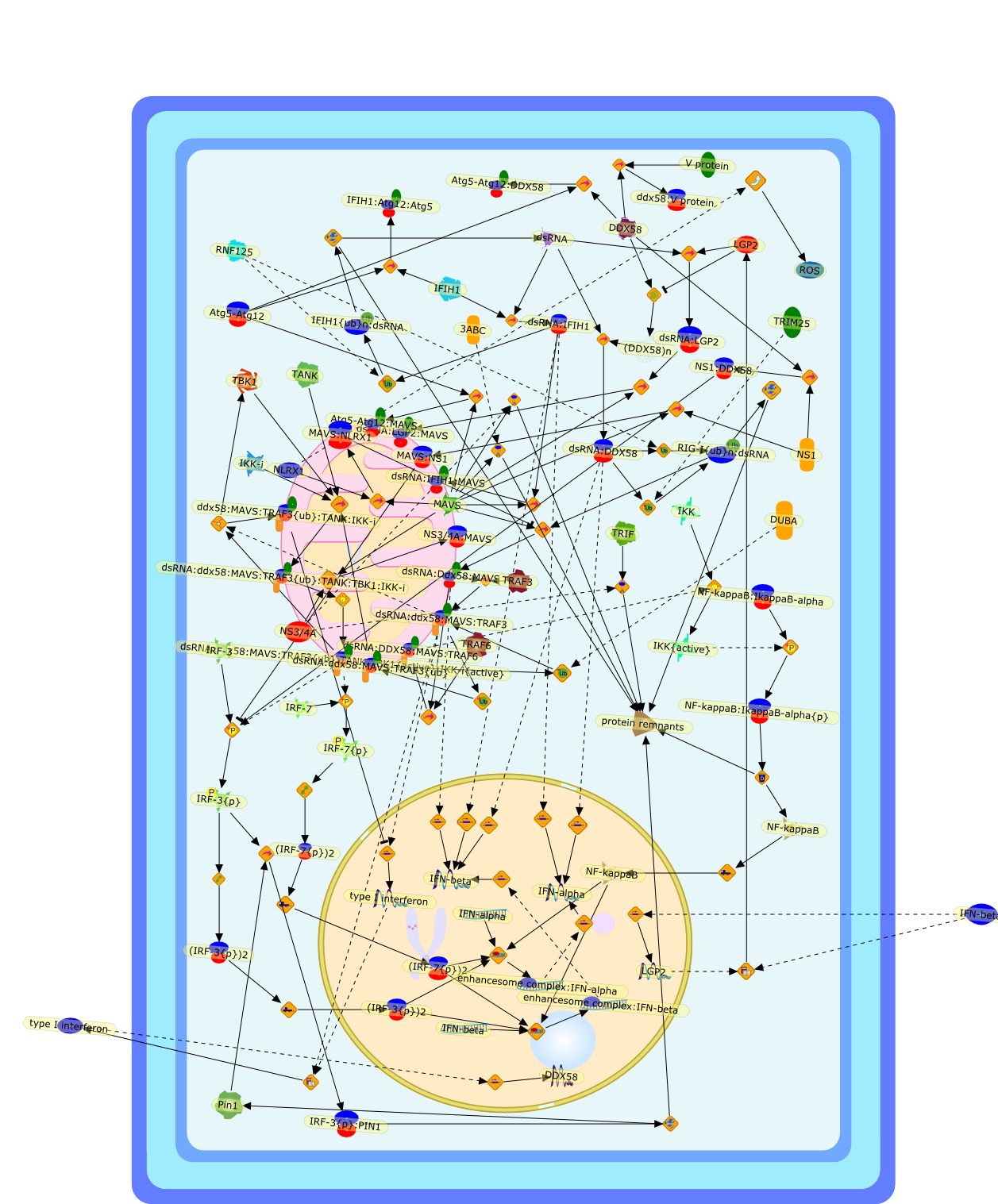
Mitochondrial antiviral immunity involves the detection of viral RNA byintracellular pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) belonging to the RIG-I-likehelicase family. The convergence of these and other signaling molecules to theouter mitochondrial membrane results in the rapid induction of antiviralcytokines including type-1 interferon. Here, we discuss recent studiesdescribing new molecules implicated in the regulation of this antiviralresponse.
PMID
18549796
|