| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
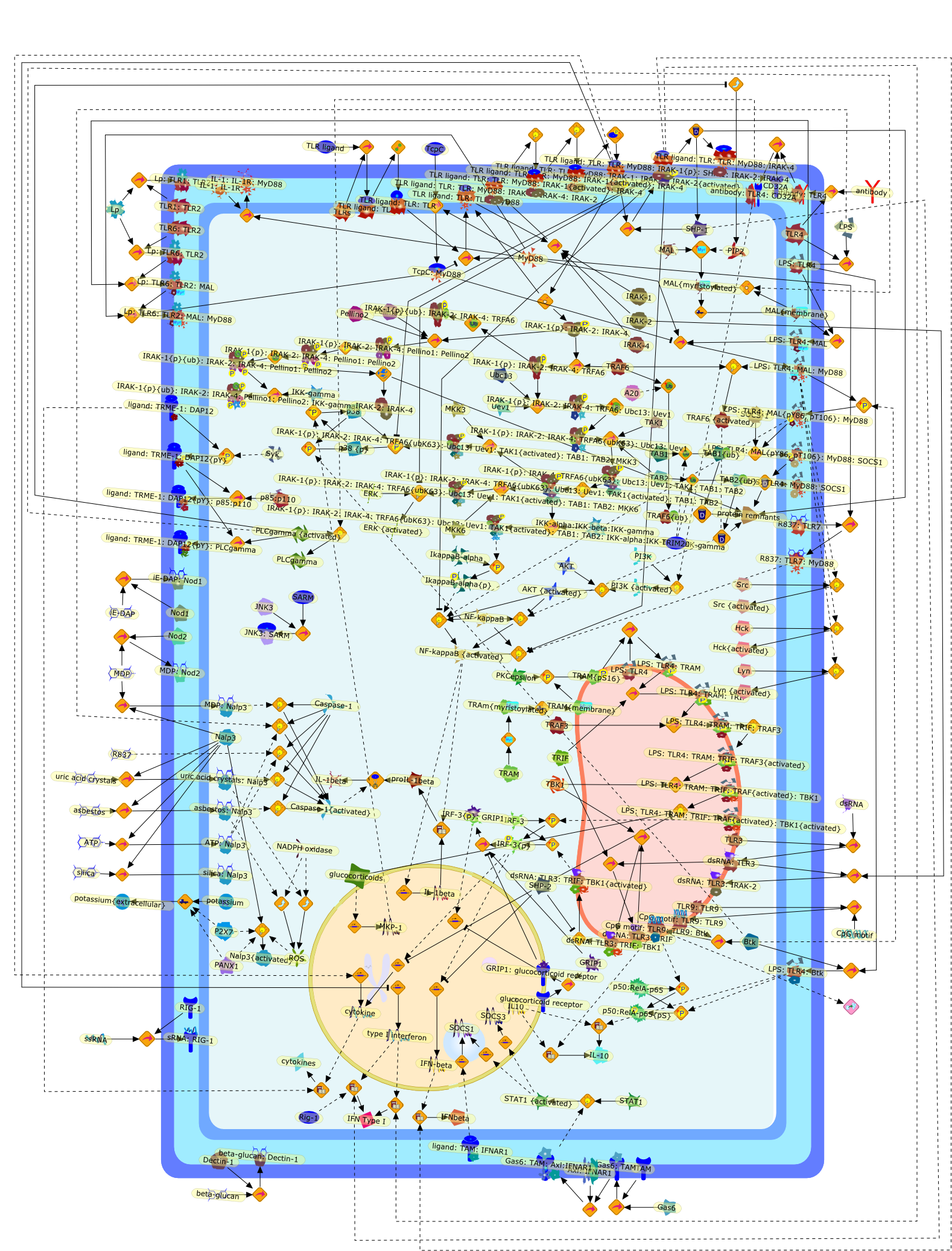
When signaling pathways collide: positive and negative regulation of toll-likereceptor signal transduction.
Affiliation
School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2,Ireland. laoneill@tcd.ie
Abstract
Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling is subjected to crosstalk from other signals,with a resulting positive or negative effect. There is complex crosstalk betweenthe NLR family of immune-regulatory molecules and TLRs, and C-type lectinreceptors such as Dectin-1 synergize with TLR2 via the tyrosine kinase Syk.Bruton's tyrosine kinase plays an important positive role in TLR signaling,whereas the TAM family of receptor tyrosine kinases is inhibitory. The tyrosinephosphatase SHP1 has been shown to positively regulate induction ofinterferon-beta, whereas SHP2 inhibits the kinase TBK1, limiting this response.K63-linked polyubiquination has also been shown to be critical for theinitiation of TLR signaling. Finally, glucocorticoids affect TLR signaling byinducing the phosphatase MKP1 and inhibiting TBK1 activation. These recentfindings emphasize the importance of considering TLR signaling in the context ofother signaling pathways, as is likely to occur in vivo during infection andinflammation.
PMID
18631453
|