| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Negative regulation of cytoplasmic RNA-mediated antiviral signaling.
Affiliation
Department of Medicine, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208, USA.
Abstract
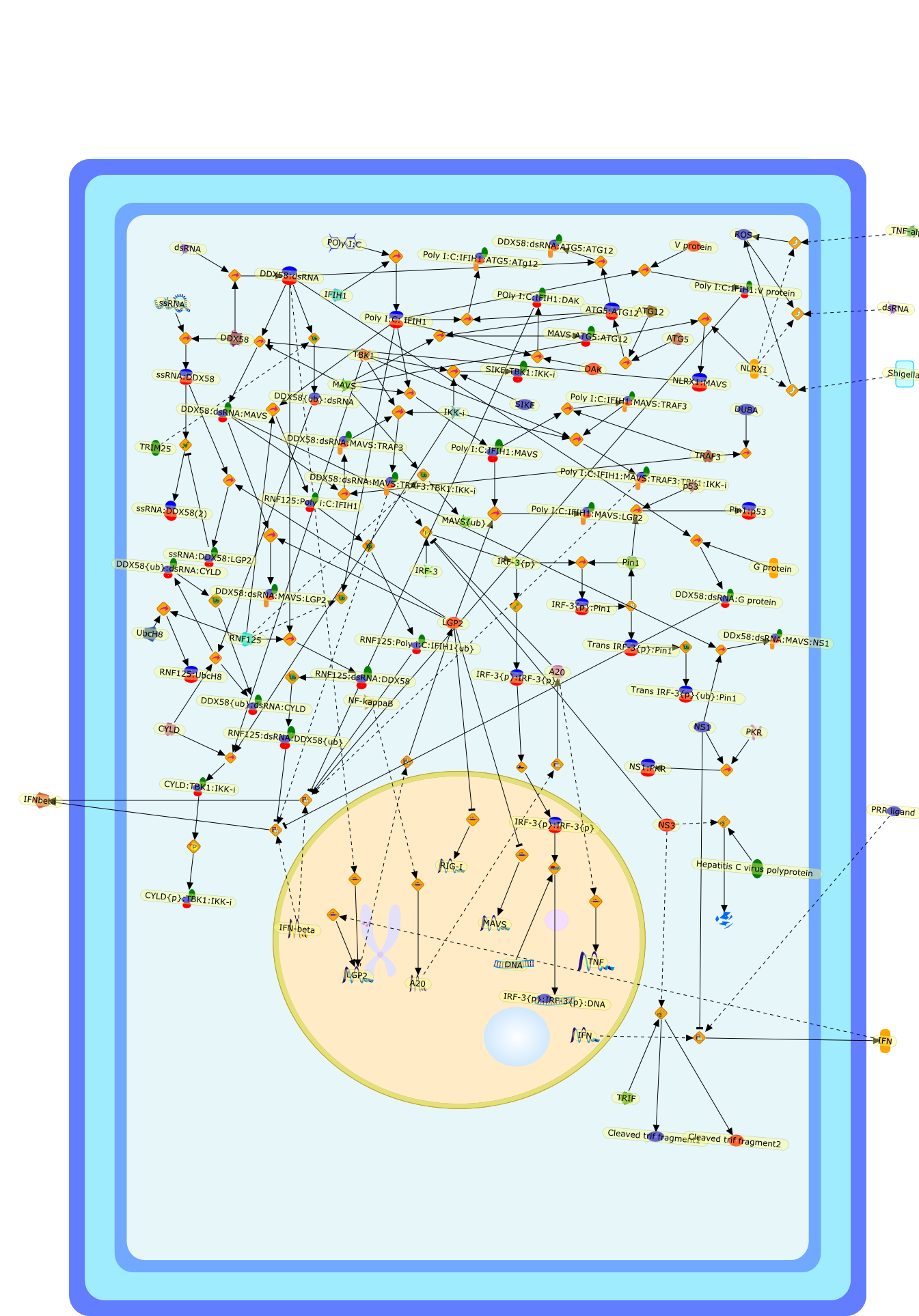
The recent, rapid progress in our understanding of cytoplasmic RNA-mediatedantiviral innate immune signaling was initiated by the discovery of retinoicacid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) as a sensor of viral RNA. It is now widelyrecognized that RIG-I and related RNA helicases, melanomadifferentiation-associated gene-5 (MDA5) and laboratory of genetics andphysiology-2 (LGP2), can initiate and/or regulate RNA and virus-mediated type IIFN production and antiviral responses. As with other cytokine systems,production of type I IFN is a transient process, and can be hazardous to thehost if unregulated, resulting in chronic cellular toxicity or inflammatory andautoimmune diseases. In addition, the RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) system is afundamental target for virus-encoded immune suppression, with many indirect anddirect examples of interference described. In this article, we review thecurrent understanding of endogenous negative regulation in RLR signaling andexplore direct inhibition of RLR signaling by viruses as a host immune evasionstrategy.
PMID
18703349
|