| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
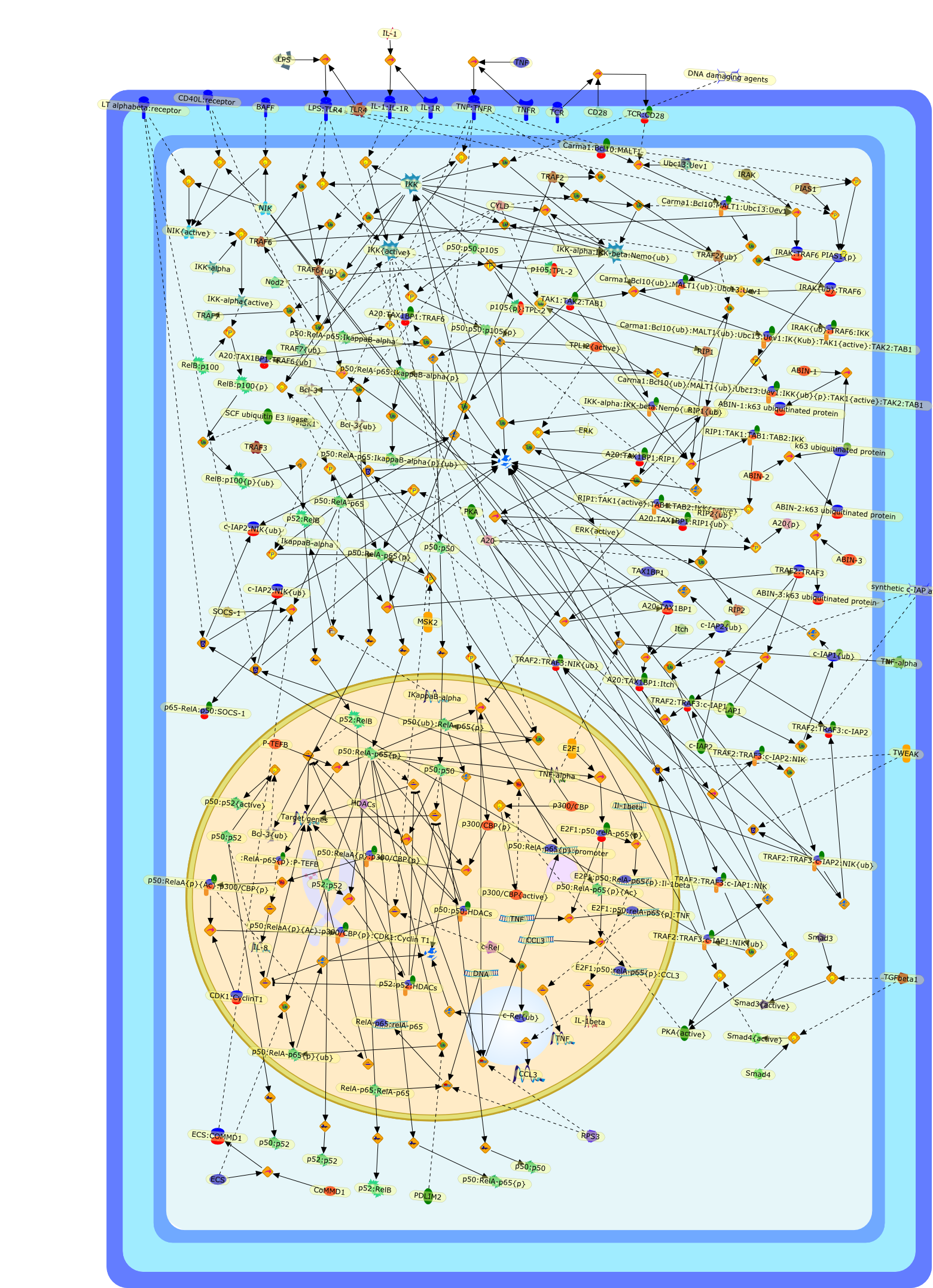
New insights into NF-kappaB regulation and function.
Affiliation
Department of Immunology, MD Anderson Cancer Center, University of Texas,Houston, TX 77030, USA. ssun@mdanderson.org
Abstract
NF-kappaB (nuclear factor-kappaB) transcription factors have multiple criticalroles in the regulation of immune responses. In unstimulated cells, NF-kappaBproteins are sequestered in the cytoplasm by IkappaB inhibitory proteins.Various immune stimuli induce the IkappaB kinase (IKK) to phosphorylateIkappaBs, triggering their ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, whichpermits nuclear translocation of associated NF-kappaB subunits and activation ofNF-kappaB target genes. Recent studies have highlighted the importance ofdynamic ubiquitination-deubiquitination events in regulating this canonicalNF-kappaB signaling pathway. Ubiquitination additionally plays critical roles inactivation of the noncanonical pathway that regulates NF-kappaB viasignal-induced processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. New research has also identifiedseveral novel regulatory proteins that control the transcriptional activity ofnuclear NF-kappaB.
PMID
18775672
|