| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Gram-negative endotoxin: an extraordinary lipid with profound effects oneukaryotic signal transduction.
Affiliation
Department of Biochemistry, Merck Sharp and Dohme Research Laboratories, Rahway,New Jersey 07065.
Abstract
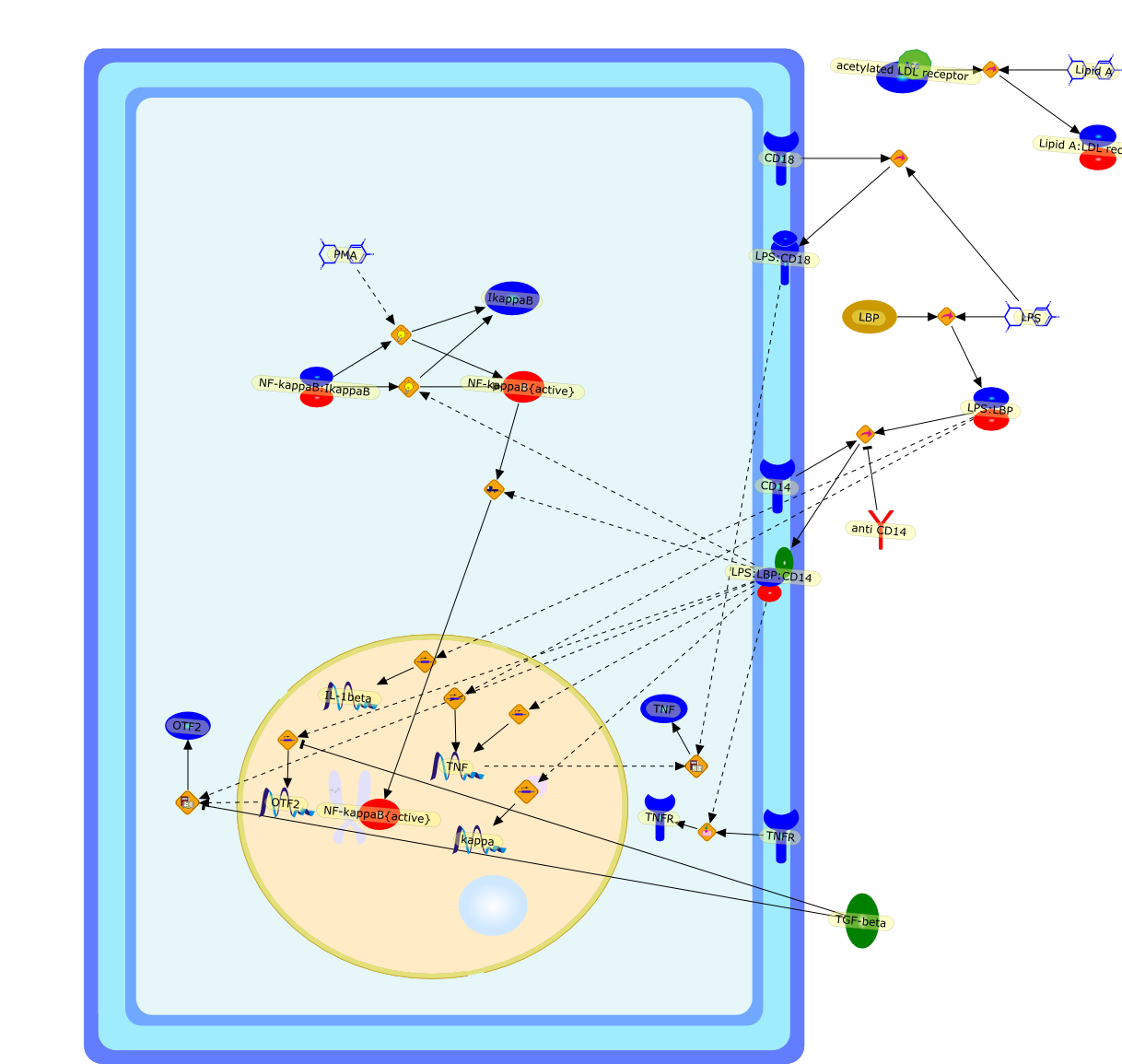
The lipid A domain of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a unique, glucosamine-basedphospholipid that makes up the outer monolayer of the outer membrane of mostgram-negative bacteria. Because of its profound pharmacological effects onanimal cells, especially those of the immune system, lipid A is also known asendotoxin. Despite decades of earlier work, the precise chemistry of endotoxinsand the biochemical pathways for their enzymatic synthesis have been elucidatedonly within the past 5 years. In this review, we summarize the essentials ofendotoxin biochemistry and also present recent experiments aimed at identifyingsurface receptors, signal-transducing elements, transcriptional factors, and keyintracellular targets involved in the response of animal cells to endotoxins.
PMID
1916089
|