| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
CD14 and other recognition molecules for lipopolysaccharide: a review.
Affiliation
Department of Anatomy and Physiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, KansasState University, Manhattan 66506, USA.
Abstract
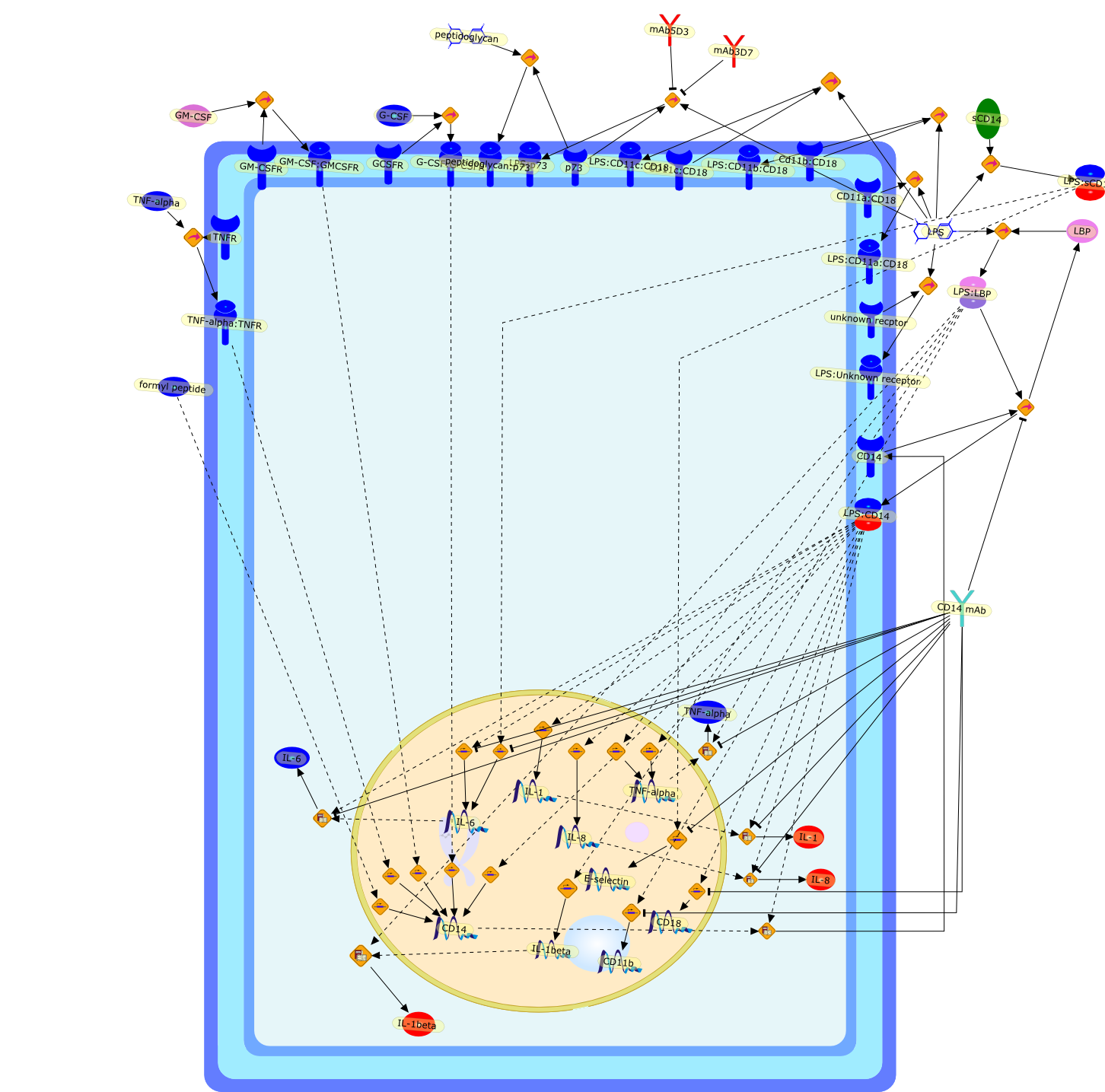
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or endotoxin elicits a broad, non-specific cascade ofevents in vivo, resulting in secretion of a variety of potent mediators andcytokines produced primarily by activated macrophages and monocytes. Theoverproduction of these effector molecules, such as interleukin-1 and tumornecrosis factor-alpha, contributes to the pathophysiology of endotoxic shock.Cellular recognition of LPS involves several different molecules, includingcluster of differentiation antigen CD14. A thorough understanding of theinteraction of LPS with cells of the immune system is necessary before effectivepreventative or therapeutic measures can be designed to limit the host responseto endotoxin. This review discusses the role of CD14 and other LPS-recognitionmolecules in LPS-mediated macrophage activation.
PMID
7542643
|