| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
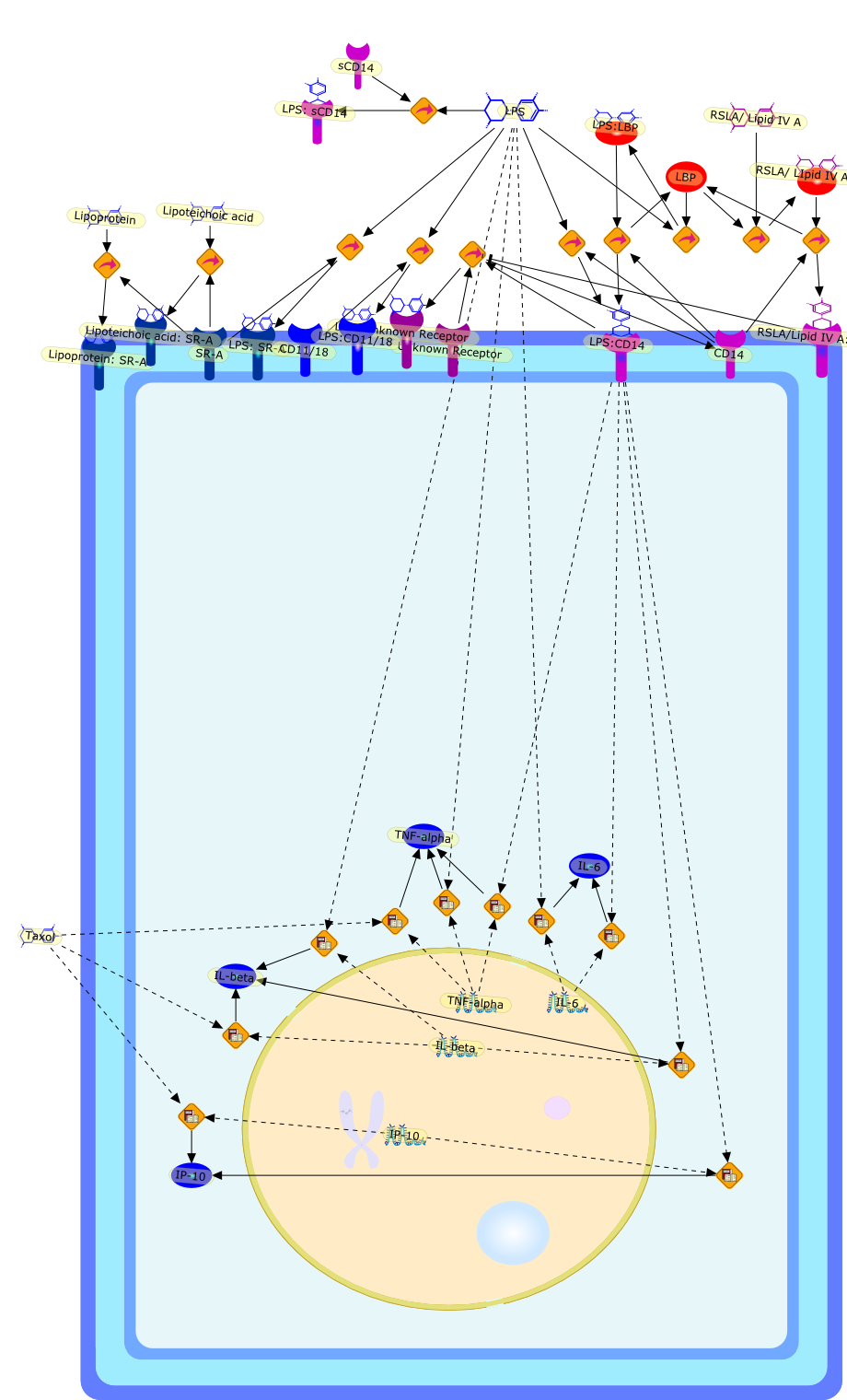
LPS-binding proteins and receptors.
Affiliation
The Pulmonary Center, Boston University School of Medicine, MA 02118, USA.mfenton@bupula.bu.edu
Abstract
Macrophage activation by gram-negative lipopolysaccharide (LPS) has beenextensively studied in an attempt to define the mechanisms that underlie innateimmunity against bacterial pathogens. Dysregulation of these same mechanismscontributes to the pathophysiological consequences of bacterial sepsis. Thebiological actions of LPS are mediated, at least in part, by both LPS-bindingproteins and LPS receptors. Several LPS receptors (CD14, the macrophagescavenger receptor, and the beta2 integrins), as well as the serum LPS-bindingprotein LBP, have been cloned and studied in detail. In addition, insightsgained through the use of LPS antagonists have led to a better understanding ofa molecule believed to function in conjunction with LPS receptors to transducesignals from the membrane to the cytosol. More recently, the use of knockoutmice has greatly expanded our knowledge of the biology of LPS receptors andbinding proteins. This review will summarize various phenotypes of mice thatlack genes encoding CD14, the scavenger receptor, and LBP. These knockout micehave revealed several unexpected features of LPS action in vivo. Together, theseanimal models may provide a means to develop and evaluate novel therapeuticapproaches to the control of endotoxin shock.
PMID
9665271
|