| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
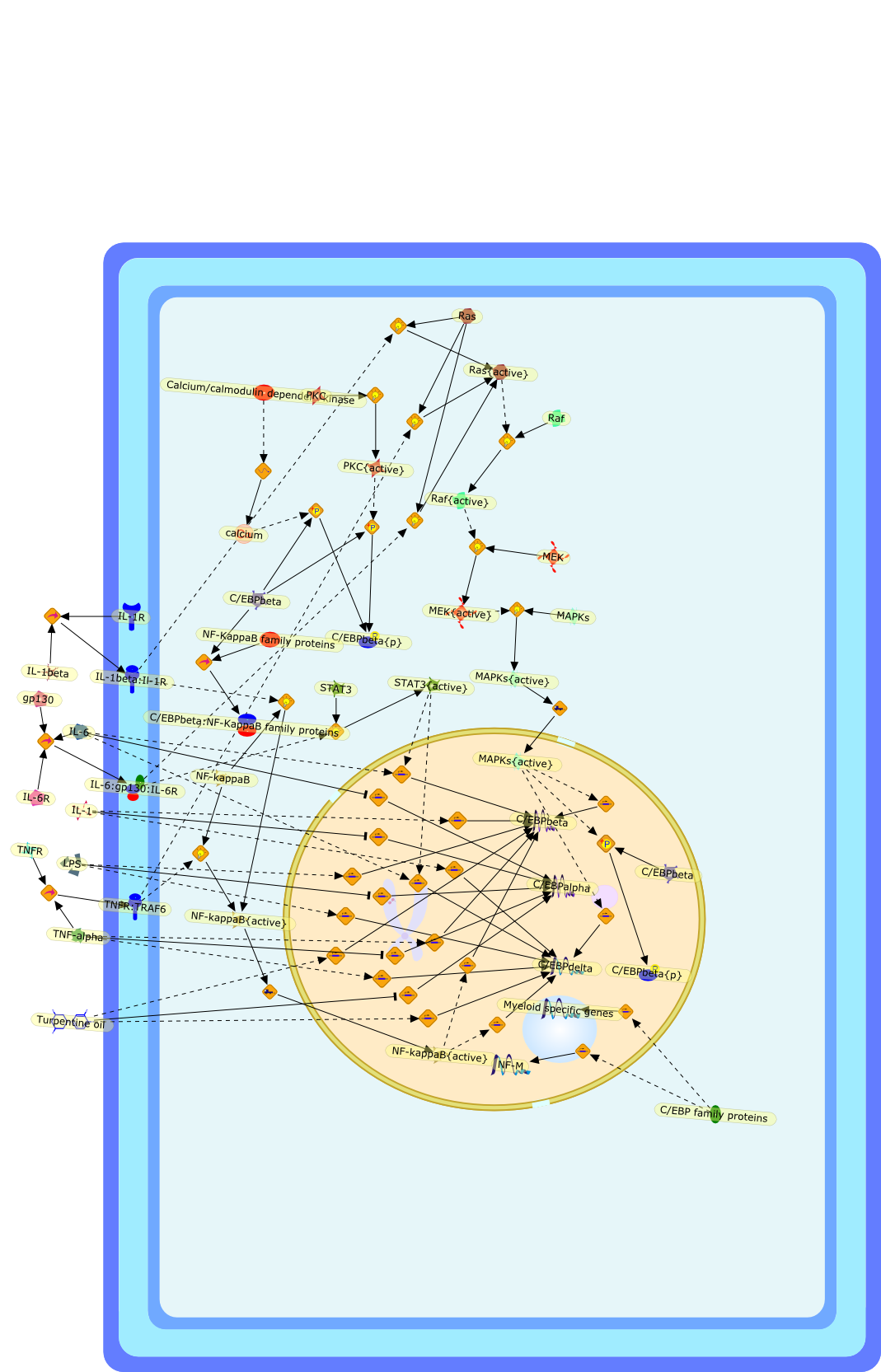
The role of C/EBP isoforms in the control of inflammatory and native immunityfunctions.
Affiliation
Department of Biochemistry, University of Dundee, Scotland, United Kingdom.vpoli@bad.dundee.ac.uk
Abstract
PMID
9792624
|