| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Afferent pathways of pyrogen signaling.
Affiliation
Department of Physiology and Biophysics, University of Tennessee, Memphis 38163,USA. blatteis@physiol.utmem.edu
Abstract
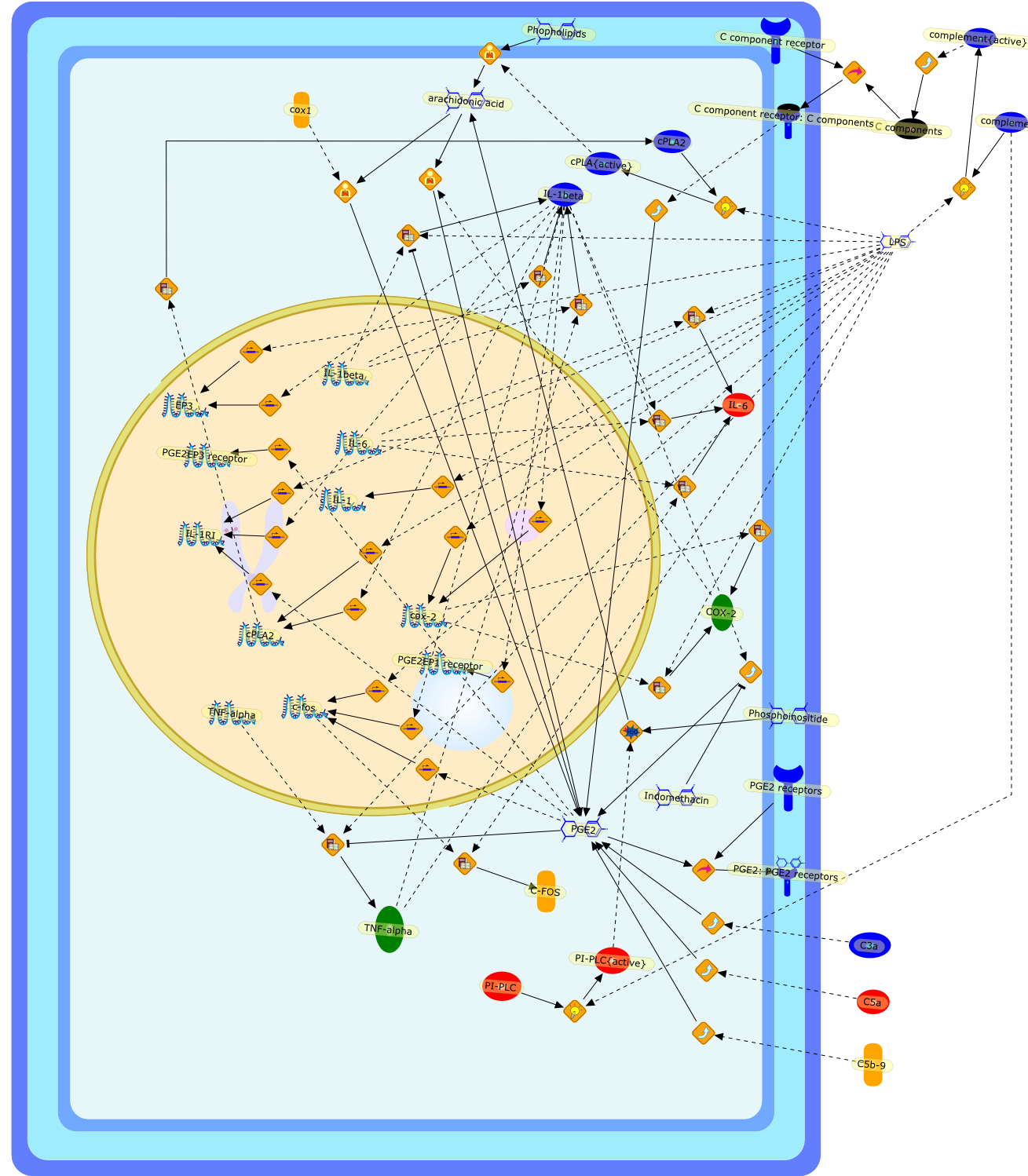
We and others recently showed that fever induced by intravenously orintraperitoneally injected lipopolysaccharide (LPS) may involve brain signalingvia hepatic vagal afferents. This suggests that LPS fever may be initiated bymediators released mainly by cells in the liver, presumably macrophages (Kupffercells, Kc). To verify this possibility, we disabled the Kc of conscious guineapigs with gadolinium chloride and monitored their core temperature andassociated preoptic prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) responses to i.v. LPS. Gadoliniumchloride pretreatment significantly attenuated both the febrile and PGE2 rises,thus supporting the hypothesis. Additionally, fluorescein-labeled LPS wasdetected in Kc 15 minutes after its i.v. administration. Paradoxically, however,the label was also present in gadolinium chloride-pretreated guinea pigs. Thus,either Kc are not the primary source of pyrogenic mediators or LPS does notprovide the stimulus for their production. Because the i.v. injection of LPSelicits virtually immediately the production of complement fragments, and Kcexpress their receptors and produce various mediators on their activation, wehypocomplemented guinea pigs with cobra venom factor. The core temperature risesproduced by i.v. LPS were reduced by complement depletions > 60%. LPS i.v. perse decreased complement, that is, complement was consumed by 12% within 10minutes. Thus, the onset of LPS fever may involve complement system and Kcactivation, but their precise roles await clarification.
PMID
9917870
|