| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Tolerance to pyrogens.
Affiliation
Physiologisches Institut, Klinikum der Justus Liebig Universitat Giessen,Germany. eugen.zeisberger@physiologie.med.uni-giessen.de
Abstract
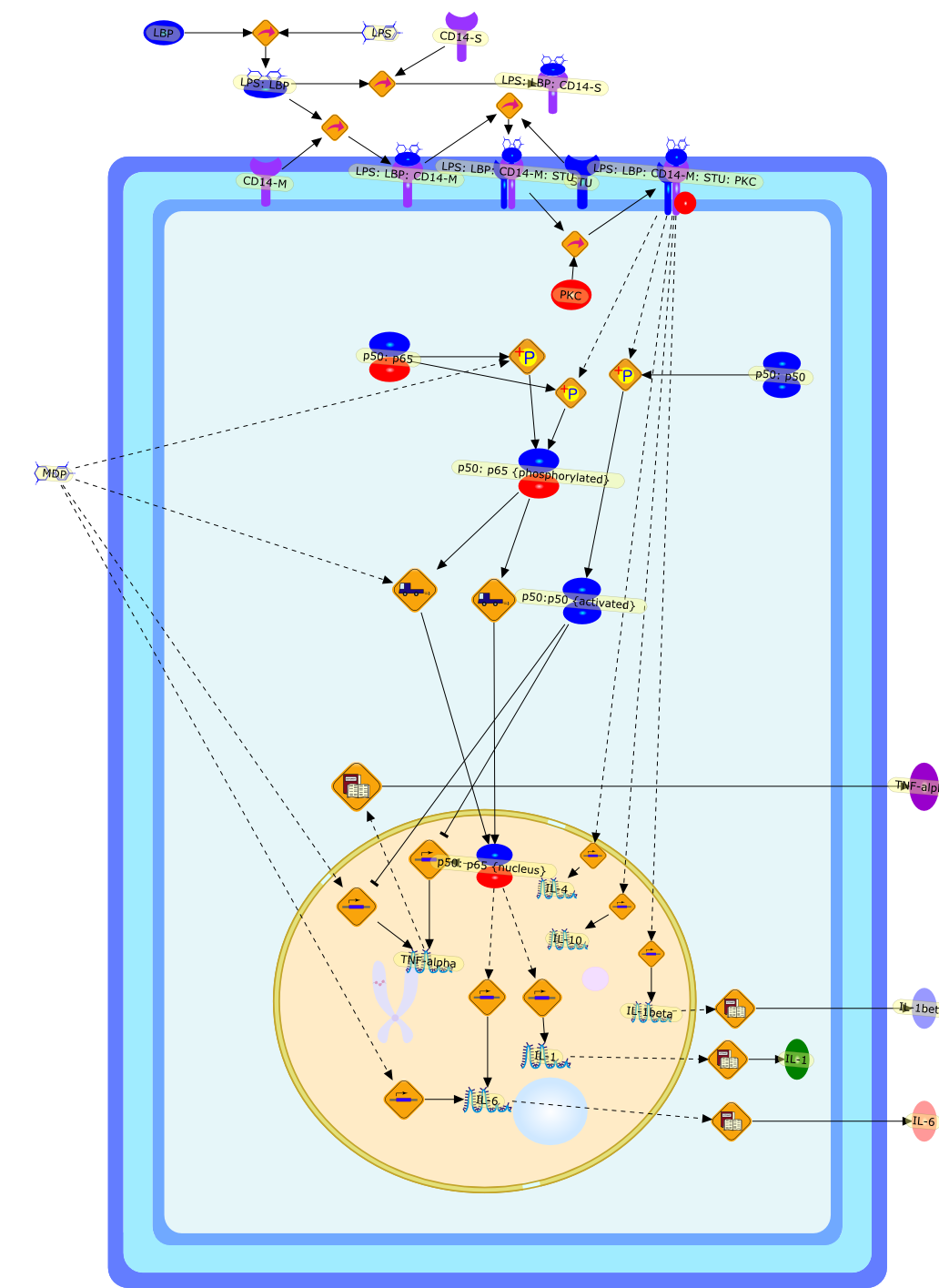
In humans or experimental animals, the repeated confrontation withlipopolysaccharides (LPS) from gram-negative bacteria, but not with muramyldipeptide (MDP) from gram-positive bacteria, leads to attenuation of almost allpathophysiologic effects mediated by proinflammatory cytokines. Our experimentsin guinea pigs and rats demonstrate that attenuation of the febrile responseduring the development of LPS tolerance is associated with a reduced productionof cytokines rather than a decrease in responsiveness to cytokines.Cross-tolerance experiments demonstrate that different stimuli influencingLPS-induced tumor necrosis factor (TNF) release and nitric oxide (NO) synthesiscan modify the development of tolerance. On the other hand, the lack ofcross-tolerance between LPS and MDP indicates that MDP can activate the cytokinecascade and induce the febrile response in animals tolerant to LPS. This mayindicate distinct receptors and signal pathways for LPS and MDP, leading toactivation of the cytokine cascade. LPS tolerance has also been demonstrated inex vivo and in vitro studies. In cultures of monocytes, diminished synthesis ofTNF and NO reported after LPS restimulation could be prevented and reversed byinterferon and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. These findingsadd an additional hypothesis in tolerance development.
PMID
9917872
|